Implicit neural radiance fields (NeRF) have established a new paradigm for scene representation, with subsequent work achieving high-quality real-time rendering. However, reconstructing 3D scenes from oblique aerial photography presents unique challenges, such as varying spatial scale distributions and a constrained range of tilt angles, often resulting in high memory consumption and reduced rendering quality at extrapolated viewpoints. In this paper, we improve MERF to accommodate the specific characteristics of oblique photography datasets to address these issues. Firstly, an innovative adaptive occupancy plane is integrated into the volume rendering process to constrain the sampling space. Additionally, we propose a smoothness regularization term for view-dependent color to strengthen the Defered MLP's ability to generalize to untrained viewpoints. Our approach, termed Oblique-MERF, surpasses the baseline method by approximately 0.8 dB, reduces VRAM usage by about 40%, and achieves higher rendering frame rates with more realistic rendering outcomes across most viewpoints.
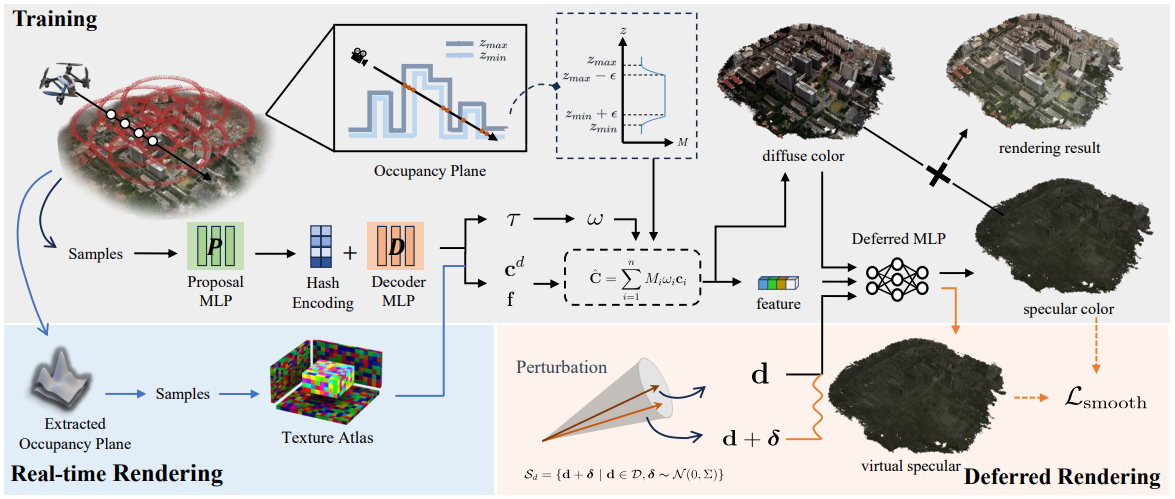
During training, we introduce a 2D plane to represent the occupied space as a sandwiched region between two height field surfaces. For sampling points on rays, occupancy masks retrieved from the occupancy plane, are used as multipliers in the volume rendering process. Additionally, we incorporate a smoothness regularization for view-dependent color to minimize variations in specular color with viewing direction. Post-training, spatial occupancy information is directly extracted from the occupancy plane, and corresponding features are stored for real-time rendering.
Campus-Oblique |
Matrix City |
We compare our Oblique-MERF with recent offline and real-time methods on Campus-Oblique and Matrix City Datasets.

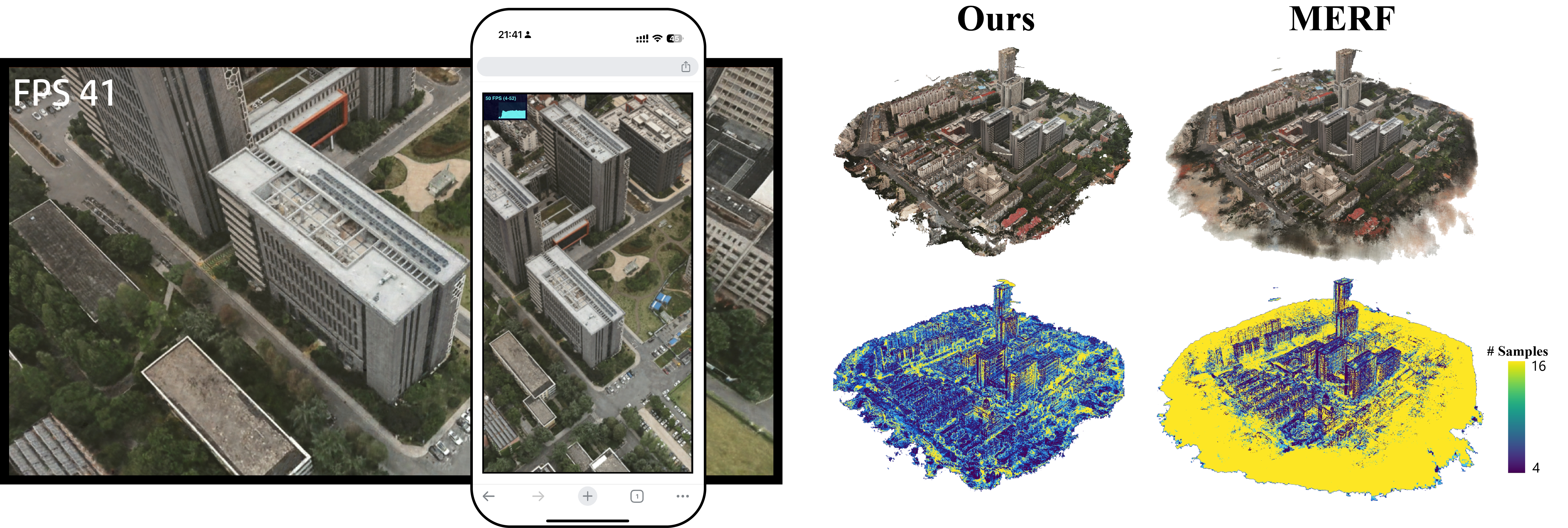
We show the visualization of Oblique-MERF and the baseline MERF for real-time rendering and sampling point distribution.
We compare the real-time rendering performance of Oblique-MERF and MERF on iPhone14 ProMax and GeForce GTX 1650.
If you find our paper useful for your work please cite:
@article{zeng2024oblique,
title={Oblique-MERF: Revisiting and Improving MERF for Oblique Photography},
author={Zeng, Xiaoyi and Song, Kaiwen and Yang, Leyuan and Deng, Bailin and Zhang, Juyong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.09531},
year={2024}
}