
Recent advances in diffusion models have made significant progress in digital human generation. However, most existing models still struggle to maintain 3D consistency, temporal coherence, and motion accuracy. A key reason for these shortcomings is the limited representation ability of commonly used control signals(e.g., landmarks, depth maps, etc.). In addition, the lack of diversity in identity and pose variations in public datasets further hinders progress in this area. In this paper, we analyze the shortcomings of current control signals and introduce a novel control signal representation that is optimizable, dense, expressive, and 3D consistent. Our method embeds a learnable neural Gaussian onto a parametric head surface, which greatly enhances the consistency and expressiveness of diffusion-based head models. Regarding the dataset, we synthesize a large-scale dataset with multiple poses and identities. In addition, we use real/synthetic labels to effectively distinguish real and synthetic data, minimizing the impact of imperfections in synthetic data on the generated head images. Extensive experiments show that our model outperforms existing methods in terms of realism, expressiveness, and 3D consistency.
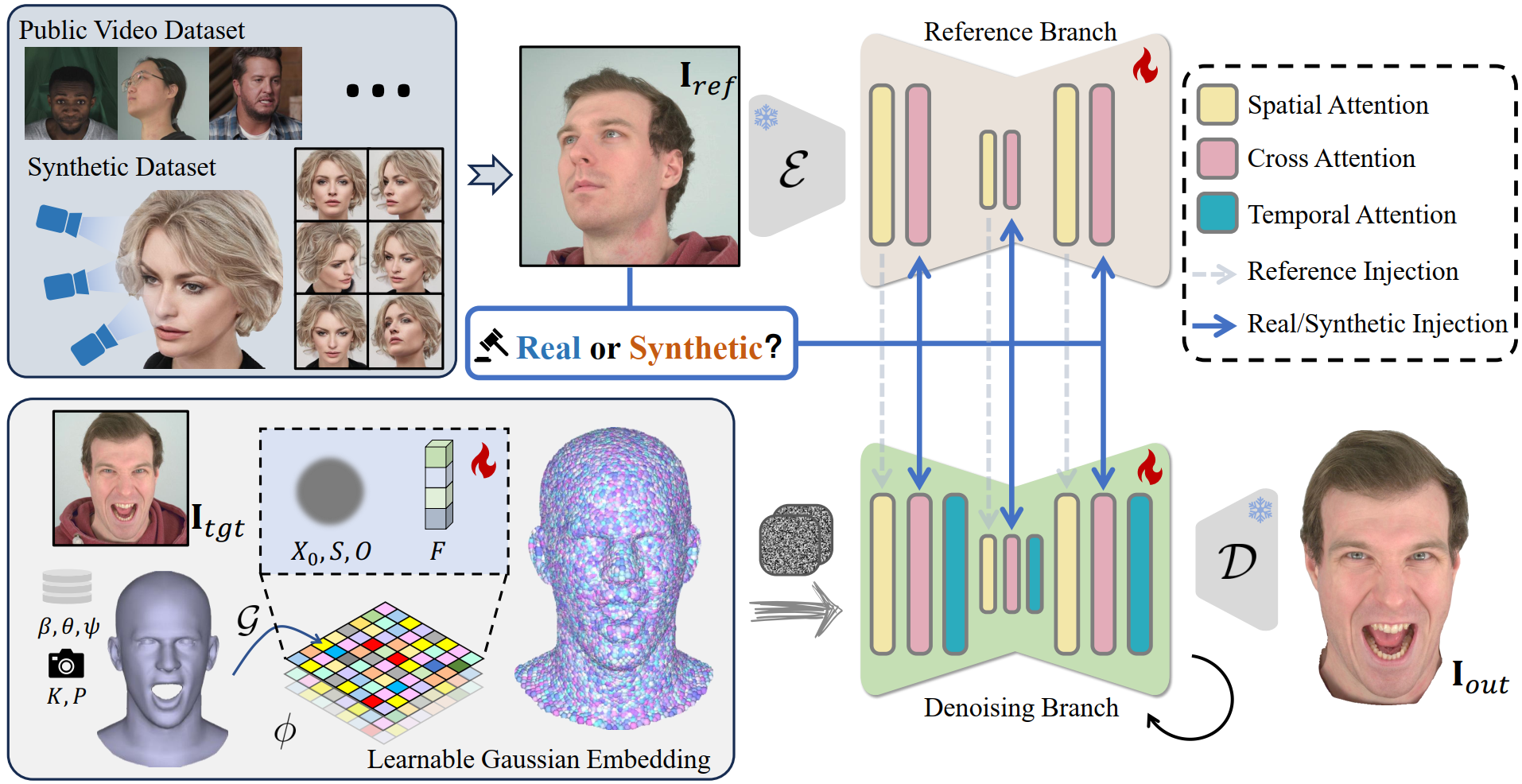
To address the limitations of existing public datasets in terms of identity diversity and pose richness, we propose to use synthetic data to improve the generalization ability and view consistency of the trained model. We first track the FLAME coefficients of the driving frames. Then the learnable Gaussians in UV space are transformed to 3D space according to FLAME UV mapping. Subsequently, the transformed Gaussians are projected and splatted to serve as control signals for a reference-guided diffusion model.
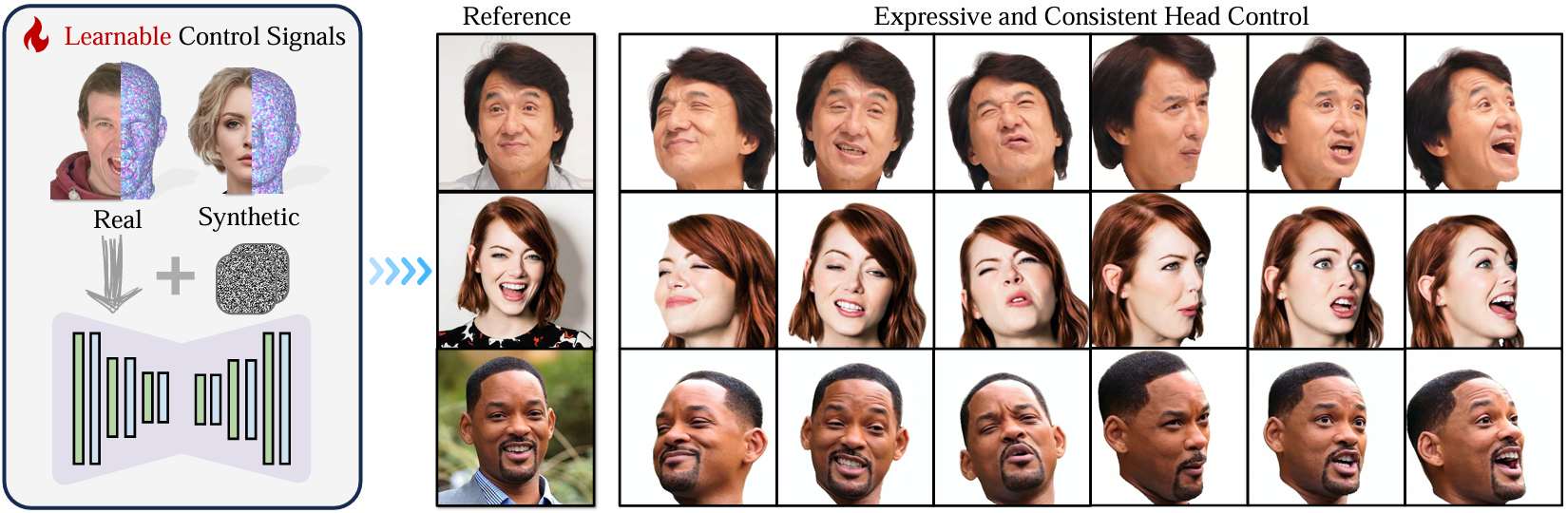
Given a single reference image, we manipulate the poses of the generated head images by adjusting the pose parameters of the FLAME head model. Our method produces reasonable and consistent results even for large pose variations. This demonstrates that our learnable Gaussian embedding, combined with training on a synthetic dataset, effectively enhances the 3D consistency of diffusion models.
We compare our work with Follow-Your-Emoji, GAGAvatar, GAGAvatar, X-Portrait, VOODOO 3D, and ROME. Our method remarkably outperforms other methods in expressiveness and consistency.
If you find our paper useful for your work please cite:
@inproceedings{Gao2025Learn2Control,
title = {Constructing Diffusion Avatar with Learnable Embeddings},
author = {Xuan Gao and Jingtao Zhou and Dongyu Liu and Yuqi Zhou and Juyong Zhang},
booktitle = {ACM SIGGRAPH Asia Conference Proceedings},
year = {2025},
}